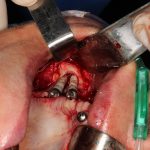
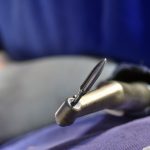
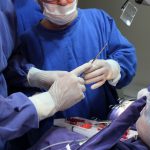
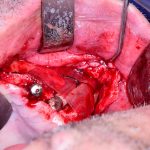
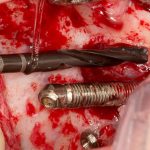
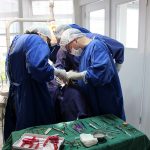
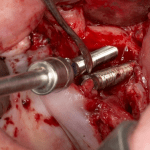
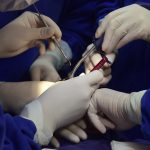
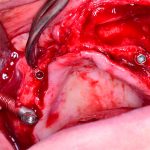
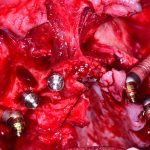
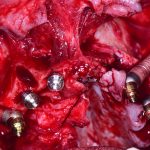
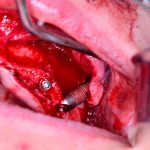
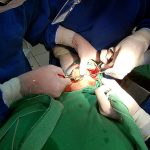
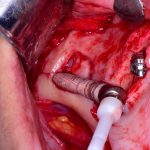
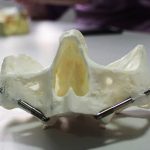
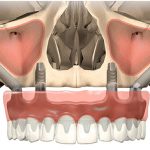
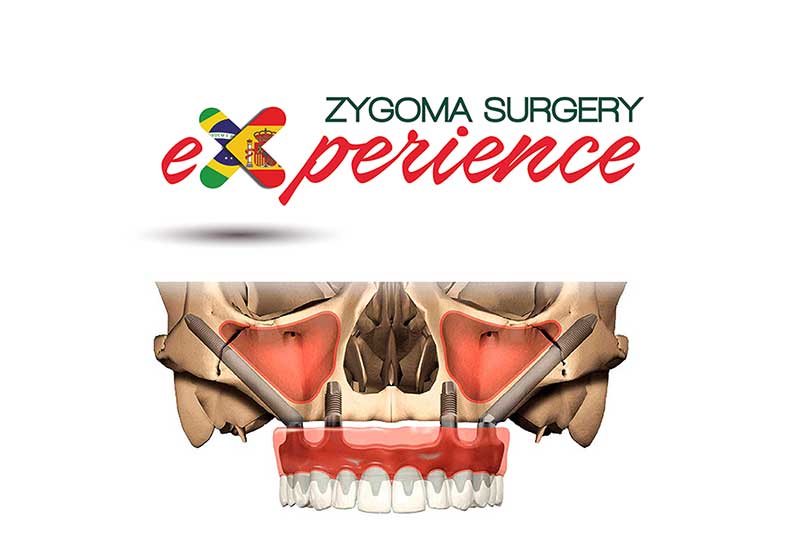
Los implantes cigomaticos (cigomáticos ó zigomáticos) son una opción de tratamiento predecible y una alternativa a los injertos en pacientes con pérdida severa de hueso. Este tipo de implante ofrece una excelente solución estética y funcional de forma inmediata.
Actualmente, esta técnica se realiza en pacientes parcial o totalmente edéntulos y en aquellos que presentan un maxilar superior atrófico severo, es decir, una ausencia total de hueso.
Están indicados en pacientes que presentan una pérdida o atrofia del hueso maxilar superior, debido a una periodontitis grave, perdida dentaría de larga evolución. La rigidez del hueso del pómulo mejora el pronóstico y seguridad del implante, reduciendo el índice de rechazo del mismo.
ARTÍCULO SOBRE PRINCIPIOS BÁSICOS EN IMPLANTES CIGOMATICOS
Table of Contents
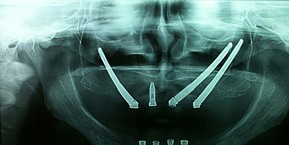
Los implantes cigomaticos son unos implantes dentales diferentes a los que se utilizan en la mayoría de pacientes. Tienen una longitud de entre 30 y 60 mm, y aunque se fijan en el hueso maxilar del paciente, su extremo superior puede llegar a situarse en el hueso malar (el hueso que se encuentra por debajo del ojo).
¿En qué casos se utilizan? Los implantes cigomáticos están indicados en casi todos los casos de falta de hueso en la zona posterior del maxilar superior. Estos implantes, tras atravesar el hueso del maxilar y el seno maxilar, se fijan en el cigoma (pómulo), donde alcanzan la máxima estabilidad. Normalmente se utiliza un implante cigomático en cada lado y de 2 a 4 implantes convencionales en el sector anterior.
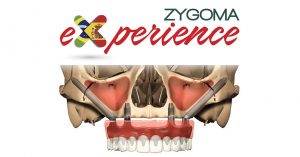
Los Implantes Cigomáticos son una alternativa a los implantes convencionales en los siguientes casos:
- En pacientes con poco hueso para colocar implantes.
- En pacientes que necesitan una cirugía de injerto óseo –como una elevación de seno maxilar o un injerto óseo en bloque.
- En pacientes que necesitan una intervención de Lefort y múltiples injertos de cresta ilíaca
- En pacientes que necesitan los dientes de inmediato.
¿Hay ventajas de los implantes cigomaticos frente al injerto de hueso?
Los implantes cigomáticos proporcionan ciertas ventajas frente a otras técnicas, sobre todo si la comparamos con técnicas en las cuales tenemos que hacer injertos de hueso al paciente.
Cuando se realiza un injerto de hueso, primero se injerta el hueso, lo que implica un tiempo de curación para que el hueso solidifique y se regenere. Posteriormente se colocan unos implantes convencionales, que requieren también tiempo de curación. Más adelante se colocarán los dientes definitivos.
La alternativa al injerto de hueso son los implantes cigomáticos. El proceso con estos implantes es más rápido, pues se pueden colocar los dientes definitivos en el mismo día o al día siguiente de colocar los implantes. Por lo tanto, reducimos mucho la duración del proceso y las molestias que ocasionamos a los pacientes. Y, sobre todo, el paciente lleva dientes fijos desde el primer día, lo que mejora la vida del paciente no solo al poder masticar sin problemas, sino también en su día a día al verse con su sonrisa definitiva.
¿De qué manera nos ayudan las nuevas tecnologías?
Las técnicas de las que disponemos hoy en día para facilitarnos las intervenciones que realizamos a nuestros pacientes de implantes cigomáticos son principalmente las dos siguientes:
La primera es el radio diagnóstico digital, con el que se reconstruye en 3 dimensiones la cara del paciente. De esta forma, se puede ver muy bien el hueso del que se dispone para poder realizar el tratamiento y así hacer una planificación previa de cómo será la intervención.
La segunda técnica y la más importante es el software de planificación digital de cirugía guiada. Este software permite colocar implantes convencionales de manera guiada mediante una férula quirúrgica que se prepara previamente.
Esto no lo vamos a poder realizar en los implantes cigomáticos, pero nos ayudará mucho a planificar los implantes en el hueso de nuestro paciente antes de intervenir y a tener una imagen fiel de cómo quedarían los implantes en la boca.
Esta técnica permite ver recorridos anatómicos, planificar la inclinación y observar las variaciones anatómicas que muchas veces nos encontramos cuando empezamos a realizar las intervenciones quirúrgicas.
Puntos clave:
Los implantes cigomaticos son una solución quirúrgica y protésica basada en la evidencia para los protocolos de dos etapas y los protocolos de carga inmediata.
Hoy en día, los implantes cigomáticos se colocan generalmente usando un protocolo de carga inmediata.
El principal caso en el que se utilizan implantes cigomáticos es en el de maxilar edéntulo severamente reabsorbido, pero también se utilizan en situaciones en las que el maxilar está parcialmente desdentado.
Entre los casos en los que se usan implantes cigomáticos se incluyen los siguientes:
- Como solución alternativa al aumento del seno
- Como rehabilitación después de la resección del tumor o un traumatismo
- En caso de fracaso de los implantes convencionales
- En caso de fallo de los injertos óseos anteriores
La colocación de implantes cigomáticos requiere una formación adecuada y experiencia quirúrgica.
Palabras clave: hueso cigomático, implantes cigomáticos, maxilar severamente reabsorbido, accesorios cigomáticos, seno maxilar.
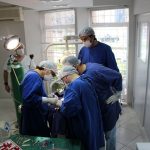
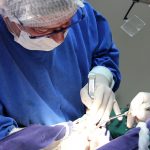
Algunas Fotos de Dental Innovation & Surgery Travel del Curso de Implantes Cigomáticos:
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
English Translation about Zygomatics Implants
The zygomatic implant is a predictable treatment option and an alternative to the grafts in patients with severe bone loss. It provides excellent results with immediate function and aesthetics. Currently, this technique is done in patients partially or totally edentulous, atrophic who have severe maxilla, ie, a total absence of bone.
These implants, after crossing the jaw bone and maxillary sinus are set in the zygomatic arch (cheekbone) location that reach maximum stability. Usually a zygomatic implant is used on each side and 2 to 4 conventional implants in the previous sector.
A dental implants are different from the ones used in most patients. They have a length of between 30 and 60 mm are fixed in the jawbone of the patient but its upper end can reach the zygoma placed. The zygomatic bone is located below the eye.
What are your instructions?
Zygomatic implants are indicated in almost all cases of lack of bone in the posterior maxilla. These implants, after crossing the jaw bone and maxillary sinus are set in the zygomatic arch (cheekbone) location that reach maximum stability. Usually a zygomatic implant is used on each side and 2 to 4 conventional implants in the previous sector. They are an alternative for the following cases:
– There is little bone to place implants.
– Patients who need a bone graft surgery, as an elevation of maxillary sinus bone graft or bloc.
– Patients requiring intervention Lefort and multiple grafts of iliac crest and for patients who need teeth immediately and can not wait 4 to 7 months without them.
What are the advantages over bone graft?
Zygomatic implants provide us certain advantages over other techniques, especially when compared to techniques in which we have to proceed to bone grafts to the patient. In the techniques that we have to proceed to bone grafts patient, systematic a bit that takes this procedure is first to graft the bone, with waiting times for that solidifies bone and forming new bone, to subsequently place a conventional implants, give another timeout so that they can then take their final teeth. The consideration is the zygomatic implants, in which in one day put the zygomatic implants and on the same day or the next day the patient can start keeping their fixed teeth on implants. Therefore, much we reduce the time and discomfort that we caused to patients. And above all we give the assurance that from the outset these patients can wear fixed teeth with which socially and when to have power will undoubtedly improve the quality that we can provide.
How new technologies help us?
The techniques available today to facilitate our interventions we make to
our patients especially zygomatic implants are twofold. A diagnosis is radius
digital we have, which, as you can see here, we can see reconstructions in 3 dimensions of the patient’s face, which we can see very well the bone we have to perform the treatment and do advance planning of how you will be our intervention. The second and most important, is the digital planning software guided surgery. This software will allow us to place conventional implants in a guided way through a surgical splint that have previously prepared. This is not going to be able to perform in the zygomatic implants, but we will help a lot to be able to plan these implants in the bone of our patient and have a true picture before you can intervene the patient how they can get these implants in the mouth. We can see anatomical tours, we will be able to plan the inclination and above all, above all anatomical variations that often we are not when we started to perform the surgery.
Key points:
Zygomatic implants are a surgical and prosthetic evidence-based solution for both two-stage and immediate loading protocols
Today, zygomatic implants are usually placed using an immediate loading protocol
The main indication for zygomatic implants is severely resorbed edentulous maxilla, but can also be used in situations partially edentulous
The indications for the insertion of the zygomatic implant include: alternative to breast augmentation, not breast augmentation, rehabilitation after tumor resection or trauma, failure of conventional implants, the failure of previous bone grafts.
Placing zygomatic implants requires proper training and surgical experience.
Keywords: zygomatic bone, zygomatic implants, severely resorbed maxilla, zygomatic accessories, maxillary sinus.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Scientific References
Esposito M, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: dental implants in zygomatic bone for the rehabilitation of the severely deficient edentulous maxilla. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;5;9
Bedrossian E, Stumpel LJ III. Immediate stabilization at stage II of zygoma implants: rationale and technique. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2001;86:10–4.
Chrcanovic BR, Abreu MH.Survival and complications of zygomatic implants: a systematic review.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013 Jun;17:81-93. Epub 2012;6. Review.
Fernández H, Gómez-Delgado A, Trujillo-Saldarriaga S, Varón-Cardona D, Castro-Núñez J.Zygomatic implants for the management of the severely atrophied maxilla: a retrospective analysis of 244 implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014 May;72:887-91.
Nakai H, Okazaki Y, Ueda M. Clinical application of zygomatic implants for rehabilitation of the severely resorbed maxilla: A Clinical Report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: 566-70.
Nkenke E, Hahn M, Lell M, y cols. Anatomic site evaluation of the zygomatic bone for dental implant placement. Clin Oral Impl Res 2003; 14:72-9.
Bothur S, Jonsson G, Sandahl L. Modified technique using multiple zygomatic implants in reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla: A Technical Note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18:902-4.
Uchida Y, Goto M, Katsuki T, Akiyoshi T. Measurement of the maxilla and zygoma as an aid in installing zygomatic implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2001;59:1193-8.
Bedrossian E, Stumpel L, Beckely M, Indersano T. The zygomatic implant: preliminary data ontreatment of severely resorbed maxillae. A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 002;17:861-
Boyes-Varley JG, Howes DG, Lownie JF, Blackbeard GA. Surgical Modifications to the Brånemark Zygomaticus Protocol in the Treatment of the Severely Resorbed Maxilla: A Clinical Report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18:232-7.
Stella JP, Warner MR. Sinus slot technique for simplification and improved orientation of zygomaticus dental implants: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15:889-93.
Puede encontrar más información sobre implantes cigomáticos en los siguientes sitios web en español y / o inglés:
COEM
SCIENCE DIRECT
SCIELO
MAXILLARIS
GACETA DENTAL

«Dental Innovation es una Start Up de Formación e Investigación al Servicio de la Odontología que nace con el Objetivo de realizar proyectos Formativos de Alta especialización y Cursos en varias disciplinas Odontológicas y ofrecer Servicios de Investigación y Publicaciones científicas, Asesoramiento Tesis, Desarrollo e Innovación en el Sector Dental.»